docs
Step 8: Binding Paths: Accessing Properties in Hierarchically Structured Models
In Step 6 , we stated that the fields in a resource model are arranged in a flat structure; in other words, there is no hierarchy of properties. However, this is only true for resource models. The properties within JSON and OData models are usually arranged in a hierarchical structure. So, let’s explore how to reference fields in a hierarchically structured model object.
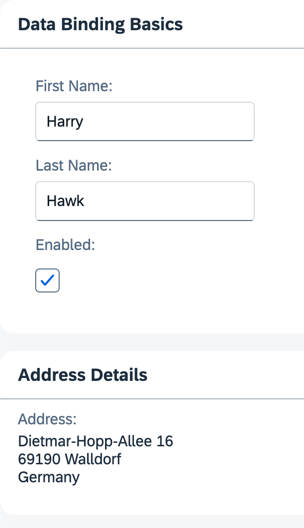
Preview
A second panel with address data is added
Coding
You can view and download all files in the Demo Kit at Data Binding - Step 8.
-
In the
data.jsonfile, add an additional sub-object namedaddress. This object has four properties:street,city,zip, andcountry.webapp/model/data.json
{ "firstName": "Harry", "lastName": "Hawk", "enabled": true, "address": { "street": "Dietmar-Hopp-Allee 16", "city": "Walldorf", "zip": "69190", "country": "Germany" } } -
Add a new panel to the
App.view.xmlwith a newLabelandFormattedTextpair of elements.The
textproperty of theLabelelement is bound to the i18n resource bundle fieldaddress.The
htmlTextproperty of theFormattedTextelement is bound to four JSON model properties:/address/street,/address/zip,/address/city, and/address/country. You can achieve the resulting address format by separating each one of these JSON model property references with a hard-coded newline character. Note thatzipandcityare separated by a space.webapp/view/App.view.xml
<mvc:View xmlns="sap.m" xmlns:form="sap.ui.layout.form" xmlns:l="sap.ui.layout" xmlns:mvc="sap.ui.core.mvc"> <Panel headerText="{i18n>panel1HeaderText}" class="sapUiResponsiveMargin" width="auto"> <form:SimpleForm editable="true" layout="ColumnLayout"> <Label text="{i18n>firstName}"/> <Input value="{/firstName}" valueLiveUpdate="true" width="200px" enabled="{/enabled}"/> <Label text="{i18n>lastName}"/> <Input value="{/lastName}" valueLiveUpdate="true" width="200px" enabled="{/enabled}"/> <Label text="{i18n>enabled}"/> <CheckBox selected="{/enabled}"/> </form:SimpleForm> </Panel> <Panel headerText="{i18n>panel2HeaderText}" class="sapUiResponsiveMargin" width="auto"> <content> <l:VerticalLayout> <Label labelFor="address" text="{i18n>address}:"/> <FormattedText class="sapUiSmallMarginBottom" htmlText="{/address/street}<br>{/address/zip} {/address/city}<br>{/address/country}" id="address" width="200px"/> </l:VerticalLayout> </content> </Panel> </mvc:View> -
Update the
i18n.propertiesandi18n_de.propertiesfiles as shown below.webapp/i18n/i18n.properties
# Field labels firstName=First Name lastName=Last Name enabled=Enabled address=Address # Screen titles panel1HeaderText=Data Binding Basics panel2HeaderText=Address Detailswebapp/i18n/i18n_de.properties
# Field labels firstName=Vorname lastName=Nachname enabled=Aktiviert address=Adresse # Screen titles panel1HeaderText=Data Binding Grundlagen panel2HeaderText=Adressdetails
Note:
The resource bundle files now contain new properties for the address and a new panel header text. Both panel properties are numbered.
In the XML view, inside the curly brackets for the binding path of the
htmlTextelement, you’ll notice that the first character is a forward slash. This is necessary for binding paths that make absolute references to properties in JSON and OData models, but you must not use it for resource models. After the first forward slash character, the binding path syntax uses the object name and the property names separated by forward slash characters ({/address/street}).Remember, all binding path names are case-sensitive.
Parent topic:Data Binding Tutorial
Next:Step 7: (Optional) Resource Bundles and Multiple Languages
Previous:Step 9: Formatting Values
Related Information